
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has approved the third installment of $1.15 billion under a broader $4.7 billion loan program for Bangladesh. This approval follows the successful staff-level agreement reached in May 2024 between the IMF delegation and Bangladeshi authorities on the policies required to complete the second review of Bangladesh’s program. This program is supported by the IMF’s Extended Credit Facility (ECF), Extended Fund Facility (EFF), and Resilience and Sustainability Facility (RSF). The completion of the second review unlocks Special Drawing Rights (SDR) of 704.70 million (approximately $932 million, equivalent to 66% of quota) under the ECF/EFF and SDR 166.68 million (about $220 million, equivalent to 15.6% of quota) under the RSF. This combined total of about $1.15 billion is now accessible to Bangladesh, further bolstering the country’s economic stability and growth prospects.
The approval of the third installment of the IMF loan, amounting to $1.15 billion, is of critical importance to Bangladesh for several reasons. First, it reinforces the country’s economic stability amid global uncertainties and domestic challenges. The funds will support Bangladesh’s ongoing efforts to sustain growth, projected by the IMF at 6.6% for the fiscal year 2024-25, closely aligning with the government’s target of 6.75%.
Secondly, the financial support from the IMF will help Bangladesh implement crucial reforms aimed at boosting sustainable revenue generation. This includes new tax policies and measures to improve public expenditure efficiency, reducing fiscal risks, and ensuring that funds are directed towards essential social welfare and development initiatives.
Furthermore, the deal emphasizes the need for subsidy reforms and better fiscal management. By cutting back on subsidies and enhancing expenditure efficiency, Bangladesh can reallocate resources to more productive sectors, fostering long-term economic growth and stability. These reforms are essential for maintaining a resilient financial sector, supporting economic activities, and ensuring overall macroeconomic stability.
Why Has the IMF Approved the Third Installment of Loan to Bangladesh?
The IMF has projected Bangladesh’s GDP growth at 6.6% for the fiscal year 2024-25, aligning closely with the Bangladesh government’s target of 6.75%. This projection reflects a positive outlook for the country’s economic trajectory, even though the IMF has slightly lowered its growth forecast for the current fiscal year (FY24) to 5.7%, down from previous estimates. Despite global economic uncertainties, Bangladesh’s economy shows resilience and the potential for steady growth, which justifies continued financial support.
The continuous growth of Bangladesh’s economy showcases some promising trends. The government of Bangladesh has undertaken various initiatives to counteract challenges, including fiscal measures, monetary policy adjustments, and structural reforms aimed at stabilizing the economy and fostering growth. The IMF’s continued support through loan installments is critical in providing the necessary financial backing and policy guidance to navigate these challenges.
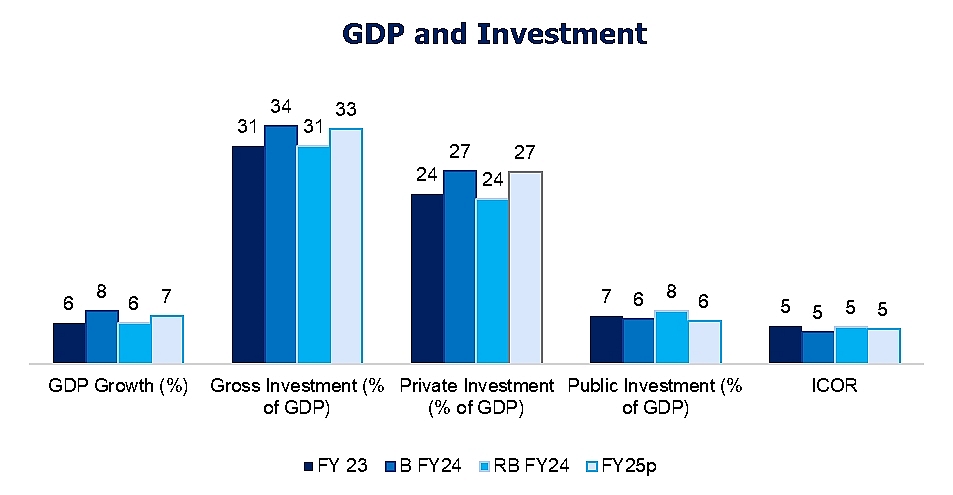
Figure: Bangladesh’s Macroeconomic Overview
Sustainable Revenue Generation
Sustainable revenue generation is essential for Bangladesh to bolster investments in social welfare and development initiatives. The IMF has emphasized the need for Bangladesh to prioritize sustainable revenue generation to support these initiatives. This involves implementing effective tax policies and administrative measures in the budget for the upcoming financial year to augment tax collections.
The FY2024-25 budget of Bangladesh includes several new tax policies recommended by the IMF. One significant change is the adjustment of the tax structure to provide some relief for upper-income individuals by raising the 10% tax slab threshold from BDT 750,000 to BDT 850,000. Additionally, the highest tax rate for top earners has been increased from 25% to 30%. These measures aim to augment tax revenues by 0.5% of GDP.
Enhanced Social Welfare Investments
The budget allocation for the Ministry of Social Welfare has been increased to Taka 12,869 crore for FY2024-25, which is Taka 1,317 crore higher than the allocation in the revised budget for FY2023-24. This increase reflects the government’s commitment to enhancing social welfare programs and supporting vulnerable populations. To ensure sustained revenue generation, the IMF has suggested that Bangladesh adopt a medium- and long-term revenue strategy. This strategy should include an implementation framework to guide future reforms and ensure that revenue targets are met consistently.
Subsidy Reforms and Fiscal Management
Reducing subsidies is a critical component of the IMF’s recommendations. By cutting back on subsidies, the government can reallocate resources to more productive uses, such as infrastructure development and social programs. This approach helps in managing fiscal risks and improving expenditure efficiency. The IMF has stressed the importance of efficient public expenditure and fiscal risk management. Improving the efficiency of public expenditure is essential for maximizing the impact of government spending. This involves better targeting of subsidies, reducing waste, and ensuring that public funds are used effectively to achieve desired outcomes. Efficient expenditure management can free up resources for investment in critical areas such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
Strengthening the governance of institutions responsible for public spending is vital for ensuring the successful implementation of the budget. This includes enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficiency in public financial management. Robust governance structures can prevent corruption, improve service delivery, and build public trust in government institutions.
Banking Sector Reforms
Reducing vulnerabilities in the banking sector remains a priority for the IMF. The banking sector is crucial for supporting economic growth by providing financing to businesses and individuals. However, vulnerabilities such as high levels of non-performing loans (NPLs) can undermine the stability and efficiency of the banking system. Implementing a strategy to reduce non-performing loans is essential for improving the health of the banking sector. High NPLs can erode bank profitability, limit lending capacity, and increase financial risks. The IMF has recommended measures such as improved loan monitoring, better credit risk assessment, and enhanced recovery processes to address the NPL issue.
Bangladesh Bank should continue transitioning to risk-based supervision to enhance financial sector resilience. Risk-based supervision involves focusing regulatory oversight on areas with the highest risk, thereby improving the effectiveness of supervision and reducing the likelihood of financial crises. Legal reforms to improve corporate governance and regulatory frameworks are essential for ensuring the stability and integrity of the banking sector. Strong corporate governance practices can prevent misconduct, enhance accountability, and promote sustainable banking practices.
Bangladesh has undertaken critical reforms to address macroeconomic imbalances. These include realigning the exchange rate, adopting a crawling peg regime, and fully liberalizing retail interest rates. These reforms are essential for maintaining macroeconomic stability and promoting sustainable growth. The IMF’s continued support is crucial for sustaining the reform momentum and managing inflationary pressures effectively.
The relationship between Bangladesh and the IMF is a testament to the mutual commitment towards fostering sustainable economic development. The implementation of crucial reforms, such as effective tax policies, enhanced social welfare investments, and efficient fiscal management, aligns with the IMF’s recommendations and demonstrates Bangladesh’s dedication to long-term economic stability. Additionally, the focus on reducing banking sector vulnerabilities and improving governance structures showcases the country’s proactive approach to addressing macroeconomic imbalances.
This partnership is not just about immediate financial assistance; it is about laying the groundwork for future economic growth. By adhering to the IMF’s guidance and implementing necessary reforms, Bangladesh is positioning itself for a prosperous future. The continued support from the IMF will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the country’s journey towards achieving sustainable development and economic resilience.
To summarize, the IMF’s approval of the third installment of its loan to Bangladesh underscores the significant progress made by the country in implementing critical economic reforms. By focusing on sustainable revenue generation, reducing subsidies, improving fiscal management, and addressing banking sector vulnerabilities, Bangladesh is laying the foundation for long-term economic stability and growth. The continued support and guidance from the IMF will be crucial in navigating the challenges ahead and ensuring that the country remains on a positive growth trajectory.
– S. M. Saifee Islam is a Research Associate at the KRF Center for Bangladesh and Global Affairs (CBGA).







